

A pilot study on 10 patients were conducted to show the efficacy of this new Faisal technique before subjecting all the volar Barton fracture presenting to us to this treatment. All patients presented to accident and emergency or outdoor of Mayo Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan, within a week of volar Barton fracture with no co-morbid condition were included in this study. This Quasi experimental study was conducted in Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Unit-I, King Edward Medical University from August 2015 to August 2016. This method is very cost effective as it save time, money and resources. With this technique, all the patients escapes a major surgery with no incision and scar. We have conducted this pilot study to assess the efficacy of our new Faisal’s technique in treating such fracture. Initially the treatment of volar Barton fracture was with closed reduction but now the treatment is shifting towards open reduction and internal fixation with early mobilization of these periarticular fracture ( 5, 6 ). Different author advocates the advantage of treatment option used by them. ( 4 )ĭifferent forms of treatment options are suggested for this type of fracture. This fracture pattern is usually seen in young active adults and is indicative of high energy trauma. Volar Barton’s fracture is the displaced intra-articular coronal plane fracture-subluxation of volar lip of the distal radius with displacement of carpus with the fragment.
#BARTON VS COLLES FRACTURE TRIAL#
There were no loss of reductionĬonclusion: Our pilot study demonstrates good result with CRPCP (Faisal’s Technique) in volar Barton’s fracture and warrants further randomized control trial study to establish its efficacy in such cases.ĭistal radius fracture comprises of 8-15 % of all the fracture encountered in emergency and approximately 60% of them are the intra-articular fracture ( 1-3 ). We had two cases (20%) with pin-tract infection that were managed with dressing and oral antibiotics according to culture and sensitivity. There were 20% (n=2) cases with excellent and 80% (n=8) cases with good outcome according to Pattee and Thompson criteria. We achieved union in 100% of the patient at mean time of 8.20 ± 0.92 weeks (7-10 weeks). Results: The mean age of total ten patients was 29.8± 3.20 years (25-35 years). Also the percentage of union and time to union were evaluated. The outcome was evaluated using Pattee and Thompson functional criteria at 6 month.
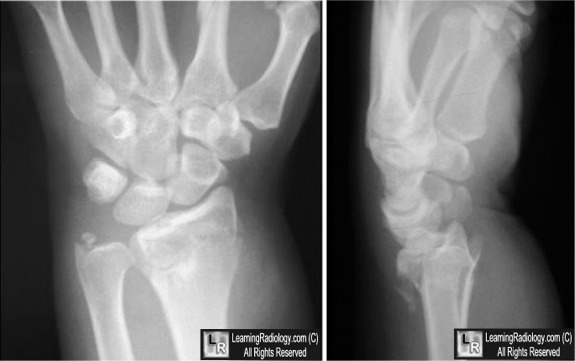
These cases, presented at our department, were managed with closed reduction under image intensifier by dorsiflexing the wrist and reducing the fragment by ligamentotaxis and percutaneous pinning in anti-glide fashion from dorsal proximal (intact cortex) aspect of distal radius and engaging the volar fragment aiming the subchondral cortex and were supplemented with short arm cast application in volar flexion. Methods: A total of 10 cases of volar Barton’s fracture fulfilling our inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in our study from August 2015 to August 2016. Abstract | This study was conducted to establish the efficacy of closed reduction and percutaneous pinning (CRPCP) in management of volar Barton’s fracture by Faisal Technique.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
